Everything You Need to Know for Radiant, Healthy Skin
Chemical peels have been used for decades to enhance skin texture, fade hyperpigmentation, and promote cell renewal. While professional treatments can deliver dramatic results, at-home peels offer a convenient and budget-friendly alternative—if done correctly. However, using them improperly can lead to irritation, burns, and long-term skin damage.
If you’re considering an at-home chemical peel, here’s everything you need to know to get all the benefits without the burn.
What Is a Chemical Peel?
A chemical peel is a treatment that exfoliates the skin by using acids to dissolve dead skin cells, revealing a brighter, smoother complexion. Unlike physical exfoliants, which use scrubs or brushes to remove dead skin, chemical peels work by loosening the bonds between skin cells, allowing them to shed naturally.
Common Acids Used in Chemical Peels
Different acids target different skin concerns. Here’s a simple guide to choosing the right one for your skin type:
For Acne-Prone Skin → Look for beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) like salicylic acid that penetrate deep into pores and help prevent breakouts.
For Hyperpigmentation & Scarring → Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) such as glycolic acid help fade dark spots and acne scars by increasing skin turnover.
For Fine Lines & Wrinkles → Lactic acid works to hydrate the skin while encouraging collagen production, improving elasticity.
For Uneven Texture & Dullness → Mandelic acid is a gentler exfoliant that smooths skin texture and brightens dull complexions.
It’s important to note that higher acid concentrations do not mean better results. More isn’t always better—sometimes, it’s riskier.
Choosing the Right At-Home Peel Format
At-home peels come in various formats, and choosing the right one depends on your comfort level and skin sensitivity.
✔ Peel Pads – Easy to use and mess-free, these are ideal for beginners and sensitive skin types.
✔ Overnight Serums – Designed for gradual exfoliation, perfect for those looking for slow, steady improvement.
✔ Toners & Peeling Solutions – These typically contain higher acid concentrations for deeper exfoliation, recommended for those with experience using acids.
✔ Multistep Kits – These offer a complete system, often including neutralizers or hydrating post-peel treatments.
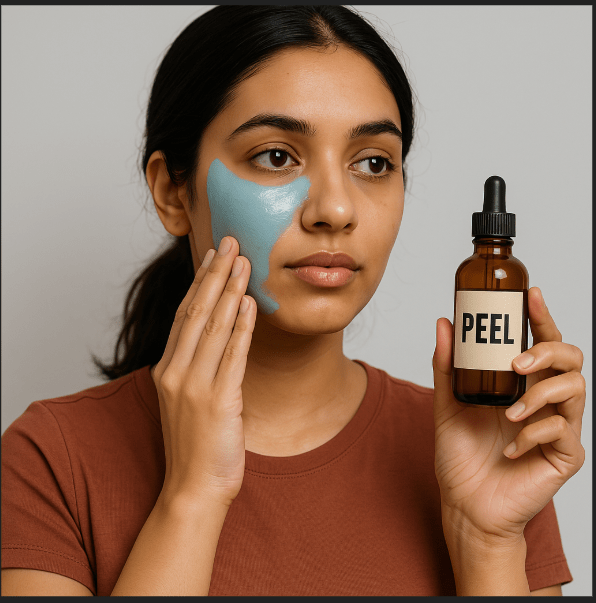

How to Safely Use an At-Home Peel
✅ 1. Perform a Patch Test
Before applying any peel to your face, test it behind your ear or on your wrist. This helps prevent unexpected reactions.
✅ 2. Start with Clean, Dry Skin
Wash your face with a gentle cleanser and pat dry before applying the peel. Avoid using any scrubs or exfoliants beforehand.
✅ 3. Apply the Peel Carefully
Follow the instructions and apply a thin, even layer, avoiding sensitive areas like the eyes, lips, and nostrils.
✅ 4. Follow the Recommended Time Limit
Leaving a peel on for too long won’t increase its effectiveness—it will only increase irritation and peeling. Stick to the recommended time.
✅ 5. Hydrate & Soothe Your Skin
After a peel, apply a hydrating serum or moisturizer with ingredients like hyaluronic acid, ceramides, or aloe vera to help calm the skin.
✅ 6. Always Use Sunscreen
Chemical peels make your skin more sensitive to UV rays, so wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) daily is non-negotiable.
What to Avoid When Using a Chemical Peel
🚫 Physical Exfoliants & Scrubs – Using scrubs on the same day as a peel can lead to over-exfoliation and irritation.
🚫 Retinoids & Strong Actives – Retinol, tretinoin, or strong vitamin C serums can increase skin sensitivity, leading to redness and flaking.
🚫 Benzoyl Peroxide & Acne Treatments – Combining peels with these ingredients can cause excessive dryness and peeling.
If you experience severe redness, burning, or prolonged irritation, stop using the product immediately and allow your skin to recover before trying another exfoliating treatment.
Which Peels Should You Avoid Using at Home?
Not all chemical peels are safe for at-home use. The FDA has issued warnings about certain products containing extremely high acid concentrations, which can cause chemical burns, deep tissue damage, and permanent scarring.
Avoid Peels That Contain:
TCA (Trichloroacetic Acid) over 10% – High concentrations should only be used by professionals.
Glycolic Acid above 30% – Can cause severe irritation and burns.
Lactic Acid above 10% – Excessive strength can disrupt the skin barrier.
100% Pure Acids – These are meant for professional use only and should never be applied at home.
For the safest results, always follow concentration guidelines and opt for reputable products with clearly labeled percentages.
Final Thoughts: Smart, Safe, and Effective Peeling
At-home chemical peels can be an amazing addition to your skincare routine when used responsibly. They help with exfoliation, acne, hyperpigmentation, and fine lines—but they must be used correctly to avoid damage.
✔ Start slow and listen to your skin.
✔ Use hydrating and barrier-repair products after your peel.
✔ Wear SPF daily to protect your new skin.
With the right approach, an at-home peel can help you achieve smooth, radiant skin—without irritation or risks.
Would you like more expert guidance on choosing the right skincare for your needs? Let AI-powered personalization help you make safe, effective beauty choices tailored just for you.
🌿 Because great skin starts with great decisions! 💖